PointRCNN
: 3D Object Proposal Generation and Detection from Point Cloud
CVPR 2019 Shaoshuai Shi • Xiaogang Wang • Hongsheng Li paper
Abstract
In this paper, we propose PointRCNN for 3D object detection from raw point cloud.
The whole framework is composed of two stages: stage-1 for the bottom-up 3D proposal generation and stage-2 for refining proposals in the canonical coordinates to obtain the final detection results.
본 논문에서는 raw point cloud에서 3D object detection를 위한 PointRCNN을 제안한다. 전체 프레임워크는 two stages로 구성된다 : bottom-up 3D proposal generation을 위한 단계-1과
최종 detection 결과를 얻기 위한 표준 좌표의 제안을 다듬는 단계-2
Instead of generating proposals from RGB image or projecting point cloud to bird’s view or voxels as previous methods do, our stage-1 sub-network directly generates a small number of high-quality 3D proposals from point cloud in a bottom-up manner via segmenting the point cloud of the whole scene into foreground points and background.
우리의 1단계 sub-network는 이전 방법처럼 RGB image 또는 projecting point cloud to bird’s view 또는 voxels에 이르는 제안을 생성하는 대신, 전체 장면의 point cloud를 foreground points와 background으로 segmenting하여 point cloud에서 small number of high-quality 3D proposals을 직접 bottom-up manner로 생성한다.
The stage-2 sub-network transforms the pooled points of each proposal to canonical coordinates to learn better local spatial features, which is combined with global semantic features of each point learned in stage-1 for accurate box refinement and confidence prediction.
Extensive experiments on the 3D detection benchmark of KITTI dataset show that our proposed architecture outperforms state-of-the-art methods with remarkable margins by using only point cloud as input.
2단계 sub-network는 ,accurate box refinement 및 confidence prediction을 위해 1단계에서 학습한 each point의 global semantic features과 결합된 더 나은 local spatial features을 학습하기 위해, each proposal의 pooled points를 표준 좌표(canonical coordinates)로 변환한다.
KITTI dataset의 3D detection benchmark에 대한 광범위한 실험은 제안된 아키텍처가 point cloud만 입력으로 사용함으로써 remarkable margins을 가진 최신 방법을 능가한다는 것을 보여준다.
The code is available at
https://github.com/sshaoshuai/PointRCNN
1 Introduction
Deep learning has achieved remarkable progress on 2D computer vision tasks, including object detection and instance segmentation etc.
Beyond 2D scene understanding, 3D object detection is crucial and indispensable for many real-world applications, such as autonomous driving and domestic robots.
While recent developed 2D detection algorithms are capable of handling large variations of viewpoints and background clutters in images, the detection of 3D objects with point clouds still faces great challenges from the irregular data format and large search space of 6 Degrees-of-Freedom (DoF) of 3D object.
Deep learnin은 object detection 및 instance segmentation 등을 포함한 2D computer vision 작업에서 remarkable 진전을 이루었다. 2D 장면 이해를 넘어, 자율 주행과 가정용 로봇과 같은 많은 실제 애플리케이션에 3D object detection는 중요하고 필수적이다. 최근 개발된 2D detection algorithms은 이미지에서 많은 다양한 viewpoints과 background clutters를 처리할 수 있지만, point clouds가 있는 detection of 3D objects는 여전히 3D object의 6 Degrees-of-Freedom (DoF)라는 불규칙한 데이터 형식과 large search space으로부터 큰 어려움에 직면해 있다.
In autonomous driving, the most commonly used 3D sensors are the LiDAR sensors, which generate 3D point clouds to capture the 3D structures of the scenes.
The difficulty of point cloud-based 3D object detection mainly lies in irregularity of the point clouds.
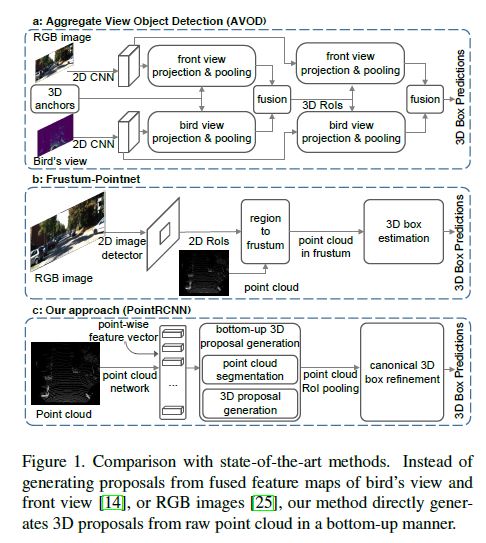
State-of-the-art 3D detection methods either leverage the mature 2D detection frameworks by projecting the point clouds into bird’s view (see Fig. 1 (a)), to the frontal view, or to the regular 3D voxels, which are not optimal and suffer from information loss during the quantization.
자율 주행에서 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 3D 센서는 LiDAR 센서로, 3D point clouds를 생성하여 장면의 3D 구조를 캡처한다.
point cloud 기반 3D object detection 어려움은 주로 point cloud의 불규칙성에 있다.
최신 3D detection methods은 optimal하지 않고 quantization 중 information loss을 겪는 bird’s view에서 point cloud( Fig. 1 (a) 참조) 또는 frontal view 또는 regular 3D voxels에 투영하는 mature 2D detection frameworks를 활용한다.
Instead of transforming point cloud to voxels or other regular data structures for feature learning, Qi et al. proposed PointNet for learning 3D representations directly from point cloud data for point cloud classification and segmentation.
As shown in Fig. 1 (b), their follow-up work [25] applied PointNet in 3D object detection to estimate the 3D bounding boxes based on the cropped frustum point cloud from the 2D RGB detection results.
feature learning을 위해 point cloud를 voxels 또는 other regular data structures로 변환하는 대신
point cloud classification 및 segmentation을 위해 point cloud data 에서 직접 3D representations을 학습하기 위한 PointNet이 제안된다.
그림 1 (b)에서와 같이, 이들의 후속 작업은 2D RGB detection results에서 cropped frustum point cloud를 기반으로 3D bounding boxes를 estimate하기위해 3D object detection 에서 PointNet을 적용했다.
However, the performance of the method heavily relies on the 2D detection performance and cannot take the advantages of 3D information for generating robust bounding box proposals.
Unlike object detection from 2D images, 3D objects in autonomous driving scenes are naturally and well separated by annotated 3D bounding boxes.
그러나 이 방법의 성능은 2D detection 성능에 크게 의존하며 obust bounding box proposals을 생성하기 위한 3D information의 장점을 취할 수 없다.
2D images에서 object detection하는 것과 달리, 자율 주행 장면의 3D objects는 annotated 3D bounding boxes로 자연스럽고 잘 구분된다.
In other words, the training data for 3D object detection directly provides the semantic masks for 3D object segmentation.
This is a key difference between 3D detection and 2D detection training data.
In 2D object detection, the bounding boxes could only provide weak supervisions for semantic segmentation.
즉, 3D object detection를 위한 training data는 3D object segmentation을 위한 semantic masks를 직접 제공한다. 이는 3D detection과 2D detection 훈련 데이터의 주요 차이점이다.
2D object detection에서 bounding boxes는 semantic segmentation을 위한 weak supervision만 제공할 수 있었다.
Based on this observation, we present a novel two-stage 3D object detection framework, named PointRCNN, which directly operates on 3D point clouds and achieves robust and accurate 3D detection performance (see Fig. 1 (c)).
이러한 관찰을 바탕으로, 우리는 PointRCNN이라는 novel two-stage 3D object detection framework를 제시하는데, 이 프레임워크는 3D point clouds에서 직접 작동하며 robust하고 정확한 3D 감지 성능을 달성한다(그림 1 (c) 참조).
The proposed framework consists of two stages, the first stage aims at generating 3D bounding box proposal in a bottom-up scheme. By utilizing 3D bounding boxes to generate ground-truth segmentation mask, the first stage segments foreground points and generates a small number of bounding box proposals from the segmented points simultaneously.
Such a strategy avoids using the large number of 3D anchor boxes in the whole 3D space as previous methods do and saves much computation.
제안된 프레임워크는 두 단계로 구성되며, 첫 번째 단계는 bottom-up scheme에서 3D bounding box proposal을 생성하는 것을 목표로 한다. 3D bounding boxes를 활용하여 ground-truth segmentation mask를 생성함으로써, 1단계는 foreground points를 segment 하고 동시에 segmented point로 부터 a small number of bounding box proposals를 생성한다 이러한 전략은 이전 방법처럼 전체 3D space에서 large number of 3D anchor boxes를 사용하지 않고 많은 계산을 절약한다.
The second stage of PointRCNN conducts canonical 3D box refinement.
After the 3D proposals are generated, a point cloud region pooling operation is adopted to pool learned point representations from stage-1.
Unlike existing 3D methods that directly estimate the global box coordinates, the pooled 3D points are transformed to the canonical coordinates and combined with the pooled point features as well as the segmentation mask from stage-1 for learning relative coordinate refinement.
PointRCNN의 두 번째 단계는 canonical 3D box refinement을 수행한다. 3D proposals이 생성된 후, 1단계부터 학습된 point representations을 풀링하기 위해 point cloud region pooling operation이 채택된다. global box coordinates를 직접 추정하는 기존 3D 방법과 달리 pooled 3D points는 canonical coordinates로 변환되고 pooled point features 및 1단계의 segmentation mask와 결합되어 relative coordinate refinement를 학습한다.
This strategy fully utilizes all information provided by our robust stage-1 segmentation and proposal sub-network.
To learn more effective coordinate refinements, we also propose the full bin-based 3D box regression loss for proposal generation and refinement, and the ablation experiments show that it converges faster and achieves higher recall than other 3D box regression loss.
이 전략은 robust 1단계 segmentation 및 roposal sub-network에서 제공하는 모든 정보를 완전히 활용한다. 보다 효과적인 coordinate refinements를 배우기 위해, proposal generation 및 refinement를 위한 full bin-based 3D box regression loss을 제안하며, ablation experiments에서는 다른 3D box regression loss보다 더 빠르게 수렴하고 더 높은 recall을 달성하는 것으로 나타났다.
Our contributions could be summarized into three-fold.
(1) We propose a novel bottom-up point cloud-based 3D bounding box proposal generation algorithm, which generates a small number of high-quality 3D proposals via segmenting the point cloud into foreground objects and background.
The learned point representation from segmentation is not only good at proposal generation but is also helpful for the later box refinement.
point cloud를 foreground objects와 background으로 segmenting하여 a small number of high-quality 3D proposals을 생성하는 novel bottom-up point cloud-based 3D bounding box proposal generation algorithm을 제안한다. segmentation을 통해 학습된 point representation은 proposal generation에 적합할 뿐만 아니라 이후 box refinement 개선에도 유용하다.
(2) The proposed canonical 3D bounding box refinement takes advantages of our high-recall box proposals generated from stage-1 and learns to predict box coordinates refinements in the canonical coordinates with robust bin-based losses.
제안된 canonical 3D bounding box refinement는 1단계에서 생성된 high-recall box proposal의 이점을 활용하고 robust bin-based losses로 canonical coordinates의 box coordinates refinements를 예측을 학습한다.
(3) Our proposed 3D detection framework PointRCNN outperforms state-of-theart methods with remarkable margins and ranks first among all published works as of Nov. 16 2018 on the 3D detection test board of KITTI by using only point clouds as input.
우리가 제안한 3D 감지 프레임워크 PointRCNN은 remarkable margins으로 최신 방법을 능가하며, 오로지 point cloud만 입력으로 사용하여 KITTI의 3D 감지 테스트 보드에서 2018년 11월 16일 현재 발표된 모든 작품 중 1위를 차지하고 있다.