Temporal Hockey Action Recognition via Pose and Optical Flows
요약
2019 CVPR workshop paper
Temporal Hockey Action Recognition via Pose and Optical Flows
human pose를 이용한 action recognition을 알아보던중 human pose와 optical flow를 이용한 다중 action을 recognition하는 논문을 찾았다.
Abstract
3가지 main components를 이용해서 hocky에 대한 action recognition 정확도를 향상시키기위해 novel two-stream acrchitecture를 고안했다.
첫째, player로부터 의미있는 단서를 추출하기위해 Part Affinity Fields model을 통해 pose를 estimate한다.
둘째, optical flow (using LiteFlownet)은 temporal features를 추출하기 위해 사용된다.
셋째, pose와 optical flow streams는 fused되고 hocky players action을 estimate하기위해 fully-connected layers로 passed된다.
새로운 사용가능 dataset은 HARPET를 만들어내었는데 이것은 sequences of annotated actions와 pose of hockey players로 구성되어있으며 hockey sticks를 human body pose으로 확장하였다.
3개의 contributions
(1) novel two-stream architecture은 optical flows를 포함하여 기존보다 약 10% 상승한 85%의 정확도를 성취하였다.
(2) hand-held objects (즉, hock sticks)의 unique localization을 part of pose로 보는것이 정확도를 13% 상승시켰다.
(3) Pose estimation을 위해 더 크고 더 일반적인 dataset인 MSCOCO를 더 작고 더 특정한 dataset인 HARPET를 transfer learning하는데 성공적으로 사용되었고 PCKh를 87%로 성취하였다.
1. Introduction
smart surveillance systems, smart elderly assistance, human-computer interaction 그리거 sports등에 넓은 applications 때문에 지난 몇년동안은 Vision-based human action recognition은 주목을 받아왔다.
lack of data, small humna size due to camera position 그리고 motion bluer from high speed human action와 같은 많은 어려움이 여러 applications에 존재한다. sports에서 알수있는 다른 어려움은 펑퍼짐한 옷과 장비 그리고 foreground와 background간의 유사성들에서 오는 noisy data라는 점이다. 앞서 언급한 모든 어려움이있는 application이 바로 ice hockey이다.
본 논문은 pose estimation과 optical flow에 고유한 high-level features를 제공하기 위해 unified된 stream actitecture에서 action recognition을 위해 pose information과 optical flow를 통합하는데 집중하며 따라서 action recognition의 전반적인 정확도를 향상한다. 또한 이것은 향상된 action recognition accuracy 하는데 있어 complementary nature of pose estimation and optical flow를 보여준다.
two-stram architecture CNN을 통해 pose와 temporal features를 분석한다. 그런다음 two strams의 outputs은 fully-connected layers를 통해 concatenated된다.
오늘날, individual players를 고려한 hockey에서 publicly available temporal action recognition datasets가 없다. 이 문제를 해결하기위해 single RGB camera로 captured된 hockey image sequences(sequences당 3개의 이미지) novel publicly available dataset인 HARPET이 사용되며 hockey stick을 포함한 18개의 joint로 구성된 pose annotation를 포함하고 있다. action은 4개의 type으로 이루어져있다: skating forward, skating backward, passing, shooting.
dataset은 class당 100 sequences 즉 전체 약 1200개의 image를 포함하고있다. HARPET 테스트에서 two-stream architecture은 약 85% end-to-end accuracy를 보인다.
Pose estimation model을 위해 적은 수의 dataset때문에, transfer learning으로 overfitting을 줄이고 PCKh@0.5에대해 87%로 효과적임을 보여준다. 또한 이전에 논문들에서는 탐험하지않은, localization of hand-held objects가 sport action recognition의 accuracy를 향상시킨다는것을 보여준다.
본 논문은 다음과 같이 구성되어있다.
Section 2, action recognition관련 논문들을 보고 two-stram-based 와 pose-based framework를 집중한다, 그리고 hockey action recognition에 대해 토의한다.
Section3에서 pose estimation과 action recognition models를 구성하는 architecture는 자세히 보여지고 수행된다.
Section 4에서 HARPET에 pose estimation과 end-to-end action recognition 모두 정확도를 평가한다.
2. Background
3. Methodology
3.1. Overview
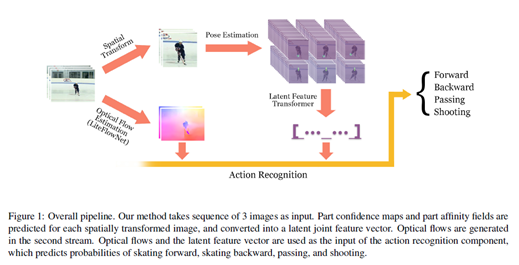
그림 1에서 보는것과 같이 전반적인 network architecture는 part affinity fields (PAFs)를 이용한 모델을 통해 pose estimatio을, LiteFlowNet을 통해 optical flow estimation을 통합하는 two-stream network를 수행하는 approach를 보여준다. network는 input으로 sequence of three images를 취하고 spatially transforming와 368x368의 pixel size의 이미지로 cropping에 의해 첫번째 stream에 사용되고 centering the person 그리고 pose estimation model에 적용한다.
그 이후, pose features는 latent feature vector layer에 concated된다.
두번째 stream은 macroscopic level의 features를 추출하기 위해 optical flow estimation을 적용한다. 두 stream 모두 주어진 sequence의 action이 classified되고 network의 output가 hocky player가 skating forward인지 skating backward인지 passing인지 shooting인지 결정된다.
3.2. Pose Estimation
Cao et al. [5]는 part affinity fields라 불리는 novel feature representation을 제안했다, 이것은 two joints간의 관련성을 평가한다. PAFs에서 각 pixel에서 2D vector는 특정 limb의 position과 orientation을 나타낸다.
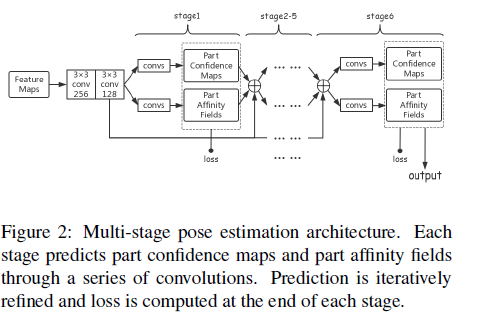
그림2는 network가 part confidence maps와 PAFs를 생성한다.
2개의 3x3 convolutions이후에 VGG-19에 의해 추출된 feature maps는 6 stages를 통과한다. 각 stage는 a series of convolutions를 통해 part confidence maps와 part affinity fields를 예측하는 two branches로 나뉜다. 그런 다음 part confidence maps와 part affinity fields 뿐만 아니라 앞서 언급한 two convoltions를 통과하는 feature maps는 모두 concatenated되고 다음 stage의 input이 된다.
Stage 1은 5개의 convolutions이고 처음 3개는 3x3의 kernel size를 사용하고 마지막 2개는 1x1의kernel size를 이용한다.
Stage 2~6은 7개의 convolutions을 가지며 처음 3개는 7x7 kernel size를 이용하고 마지막 2개는 1x1 kernel size를 이용한다. 모든 convolutions의 strides는 1이고 모든 paddings는 feature maps 크기와 같게 유지한다. prediction은 iterativelt로 refined되고 loss는 모든 stage에서 maps과 fields output으로 계산된다.
3.3. Latent Feature Transformer
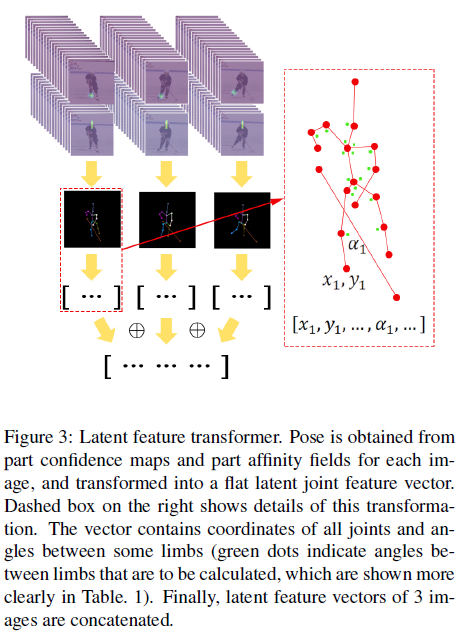
그림3은 간단히 par confidence maps와 part affinity fields을 latent joint feature vector로 transforming하는 pipeline을 보여준다.
single person의 full pose를 얻기위해, 기존의 alogrithm [Realtime multiperson 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields] 를 수정한다 먼저 limb connection 후보들을 얻고 그것들을 multiple persons의 pose에서 모은다. 각 joint에서 후보들을 threshold로 filtering하는 대신에, part confidence map에 상응하는 highest score에 2개의 peaks를 reserve(? 보류)한다. 이것은 joint를 잃지 않게 한다.
network가 때때로 실수를 하고 그리고 PAFs에 의해 제공되는 정보를 leverage하기를 원하므로 best location은 오로지 part confidence maps에 따라 결정될수 없기 때문에 highest score를 갖는 joint가 선택되지 않는다. 그런다음 single candidate는 각 joint에서 선택된다. higher value를 갖는 head top의 candidate에서 시작하고 결정된 joints에 관련된 가장 가능성이 있는 joint candidates를 interatively로 선택함으로써 그것을 full pose로 확장한다 network가 비교적 덜 실수하기때문에, limbs와 비교하여 상대적으로 쉽게 joint를 detect할수 있는 Head top은 시작 point이다.
joint candidates간의 관련된 score는 limb에 따른 PAFs에 대응하는 line integral 를 calculating함으로써 결정된다. [Realtime multiperson 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields]의 수식 (10), (11) images 3개에 모든 joints의 location을 얻은 뒤에, Fani et al. [11]에 언급된 procedure은 joints의 location들의 각각에 적용된다.
Fani et al. [11]에서 모든 images의 identified된 joints는 모든 training images에서 평균 head segment length로 scaled된다. 서로 다른 images간의 human size에 의존성의 영향을 제거하기 위해 head segment length로 각 이미지의 joints를 normalize한다. 특정 limb간의 angles는 표1과 같이 계산된다. scaled된 joint locations와 computed된 angles는 각 이미지에대한 feature vector를 형성하기 위해 concatenated된다. 이미지 3개에 대한 vectors는 size 156의 one dimensional feature vector로 concatenate한다. 이것은 action recognition component로 들어간다.
3.4. Action Recognition Component
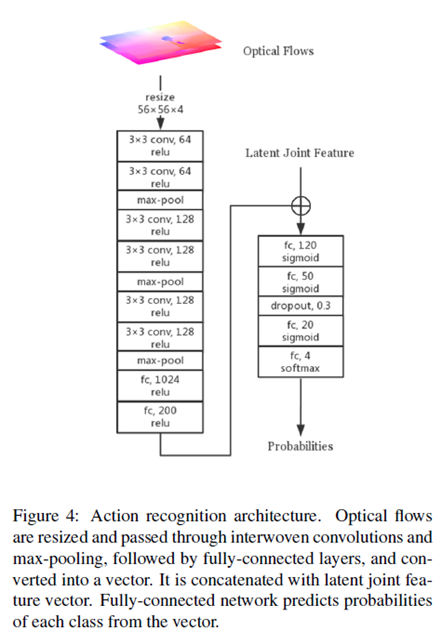
LiteFlowNet (Hui et al. [17])는 optical flow estimation에 최신 기술이다. 이 작업에서 pyramidal features는 cascaded flow inference와 반복적으로 flow fields의 resulution이 증가하는 flow regularization modules에 의해 받아진다. pre-trained된 LiteFlowNet이 사용된다. LiteFlowNet은 2개의 이미지를 input으로 받고 2개의 optical flows를 3개의 이미지에서 생성한다.
action recognition component는 joint locations와 optical flows에 의해 제공되는 정보를 leverages한다.
구조는 그림4와 같다. 획득한 optical flow fields는 4-channel map과 concatenated되고 56x56 pixels로 resized된다. 그런다음 map은 몇개의 convlutional과 max-pooling layers를 통과하고 fully-connected layers를 통과하고 flat feature vector로 converted된다. ReLu activation은 모든 convolutional과 fully-connected layers에 사용된다. optical flows에 의해 생성된 feature vector는 latent joint feature vector와 함께 concatenated된다.
latent joint feature vector와 concatenated된 flow feature vector는 4개의 fully-connected layer를 통과한다, 그것들의 처음 3개는 sigmoid activate가 있고 마지막 하나는 4개의 classes의 probabilities를 output하기 위해 softmax를 사용 dropout layer는 overfitting을 줄이기 위해 두번째 fully-connected layer (50 unit)이후에 추가된다.
3.5. Training Details
데이터셋이 작기 때문에, overfitting을 줄이기 위해 dropout, data augmentation 그리고 early stopping과 같은 다양한 methods를 사용하였다. transfer learning의 기본 method로서, pose estimation network는 MSCOCO dataset에 pre-trained된 weights를 base로 fine-tuned된다. overfitting을 피하기위해, stage 5의 마지막 3 layers를 제외하고, 모든 layeers의 weights 와 stage 6의 모든 layers는 frozen한다. 그러나, 여기서 학습하길 원하는 joints는 MSCOCO dataset과 다르다. transfer learning을 수행하기위해, 오로지 pose estimation network의 마지막 2개 stages는 다음과 같이 trained된다, stages의 나머지의 loss는 computed되지 않고 마지막 two stages는 18개의 새 joint를 output한다.
더 다양하게 나타내게 하기위해서 training시 여러 data augmentation가 수행된다. pose estimation network를 위해 원래 이미지를 랜덤으로 flipped, scaled, rotated 한다, Cao et al. [5]. 와 유사하게 action recognition network를 위해, 추가적인 methods를 추가하기 위해 pose estimation network를 적용한다.
action recognition component를 training하는동안 joint에 flipping할때마다, optical flows가 적용된다.
pose estimation network와 action recognition network는 따로따로 trainined된다.
action recognition part는 30 epochs이상이면 overfitting을 시작한다. 따라서 training 30 epochs 의 early stoppting 기술과 highest validation accuracy에 checkpoint를 picking up하는 것이 채택되었다. 만약 action recognition network에 input이 pose estimation network의 prediction 이면 train이 어렵다, 따라서 대신 joint locations의 ground truth로 augmented한 pose estimation network를 train하고 예측과 함께 검증한다. 이 network는 정확하게 localized되지 않은 joints인 경우에도 잘 generalize한다.
