EpipolarPose : Self-Supervised Learning of 3D Human Pose using Multi-view Geometry
번역
2019 CVPR paper
EpipolarPose : Self-Supervised Learning of 3D Human Pose using Multi-view Geometry
EpipolarPose
Abstract
정확한 3D human pose estimators를 training하는것은 비용을 치뤄야하는 많은 양의 3D ground-truth data가 필요하다.
다양한 Weakly 또는 self supervisied pose estimation methods는 3D data의 부족 때문에 제안된다.
그럼에도 불구하고, 추가적으로 2D ground truth poses, 이런 methods들은 다양한 형식(예,unpaired 3D gt, a small subset of labels)에서 추가적인 supervision 또는 multiview setings에 camera parameters를 요구한다.
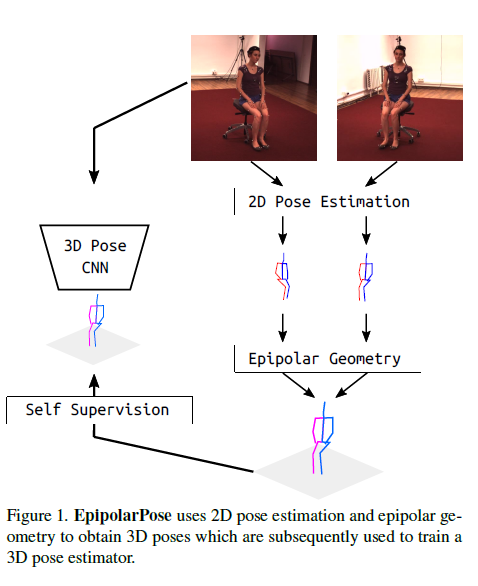
이러한 문제를 해결하기위해, 어떠한 3D ground truth data 또는 camera extrinsics가 필요없는, EpipolarPose, a self-supervised learning method for 3D human pose estimation을 제안한다.
traing 하는동안, EpipolarPose는 multi-view images에서 2D poses를 estimates하고, 그런다음 3D pose estimator를 train하기위 해 사용되는 3D pose와 camera geometry를 얻기위해 epipolar geometry를 사용한다.
우리는 우리의 approach의 유효함을 standard benchmark dataset(즉, Human3.6M과 MPI-INF-3DHP)에서 증명한다. 우리는 weakly/self-supervised methods중에 new state-of-the-art를 이뤄냈다. 더욱이 우리는 새로운 performance measure Pose Structure Score (PSS)를 제안한다, 이것은 ground truth와 관련하여 pose의 구조적 타당성을 평가하기위해 scale에 불변하고 구조 인식 측정이다.
1. Introduction
computer vison 분야에서 in the wild환경에서 Human Pose estimation은 challenging problem이다.
비록 two-dimensional (2D) pose estimation을 위한 large-scale dataset이 있지만, 3D datasets는 제안된 laboratory settings 또는 제안된 사이즈 그리고 다양성이 있다. in-the-wild에서 수집한 3D human pose annotations는 costly하고 3D datasets는 제안되어있기 때문에, researchers는 이미 존재하는 2D datasets에서 추가적인 supervision의 minimal amount를 사용함으로써 정확한 3D pose estimator를 얻기위한 목표를 가지는 weakly 또는 self supervised approaches를 목표로 한다.
다양한 방법들이 개발되어 왔다. 추가적인 ground-truth 2D poses가 필요한 methods들은 (unpaired 3D ground trtuh data, a small subset of labels와 같은) 다양한 forms 또는 multiview seeings에서 (extrinsic) camera parameters등과 같은 추가적인 supervision을 요구한다.
알다시피, 오로지 하나의 methods[9]만이 오로지 2D ground-truth만을 이용하여 3D pose estimator를 생산할 수 있다.
우리의 methods, “EpipolarPose”는 3D poses를 얻기위해, 2D pose estimation 그리고 epipolar geometry를 사용한다, 이것은 이후 3D pose estimator를 train하기위해 사용된다.
EpipolarPose는 임의의 카메라 수로 작동한다(적어도 2개) 그리고 이것은 어떠한 3D supervision 또는 extrinsic camera parameters가 필요없지만 제공된다면 사용할 수 있다.
On the Human3.6M [15] and MPI-INF-3DHP [23] datasets, we set the new state-of-the-art in 3D pose estimation for weakly/self-supervised methods.
Human pose estimation은 이후 더 높은 수준의 추론을 허용한다, 예를들어 자율주행시스템(자동차,산업로봇) 그리고 activity recognition
이런 tasks에서, pose에서 structural errors는 MPJPE(mean per joint position error)와 PCK(percentage of correct keypoints)와 같은 traditional evaluation metrics로 측정하는 localization error보다 더 중요하다.
이런 metrics는 각 joint를 독립적으로 처리하므로 전체 pose를 structure로 평가하는데 실패한다.
Figure 4는 reference pose와 관련된 같은 MPJPE를 배출하는 구조적으로 매우 다른 poses를 보여준다.
이런 문제를 해결하기위해, 우리는 pose에 structural errors에 민감한, Pose structure Score (PSS)라 불리는 new performance measure를 제안한다. PSS는 pose의 ground truth에 관련된 pose의 구조적 타당성을 score할수있는 scale invariant performance score를 계산한다.
PSS는 loss function이 아님을 알아라, 이것은 MPJPE와 PCK와 함께 사용하여 pose estimator에 의해 만들어진 structural errors를 설명할 수 있는 performance measure이다.
PSS를 계산하기 위해, 먼저 ground truth poses의 natural distribution model이 필여하다. 결과적으로, unsupervised clustering method를 사용한다.
\(p\)는 image에서 predicteed pose이고 \(q\)는 전체 ground-truth이다. 먼저, \(p\)와 \(q\)에 가장 가까운 cluster centers를 찾는다. 만일 그것들 모두 같은 clister center에 가장 가깝다면 posr structure score (PSS) of \(p\)는 1이고 아니면 0이다.
Contrivutions 우리의 contrivutions는 다음과 같다 :
- single-image에서 3D human pose를 predict할수 있는 method인, Epipolarose를 제시한다. training에서는, EpipolarPose는 어떠한 3D supervision과 camera extrinsics를 요청하지 않는다.그것은 epipolar geometry와 2D ground-truth poses를 사용하므로써 우리의 3D supervision을 생성한다.
- 3D human pose estimation에 대한 weakly/self-supervised methods 중에 new state-of-the-art를 set하였다.
- 3D human pose estimation에 대한 capture structural errors 보다 더 나은 new performance measure인, Pose Structure Score (PSS)를 제시한다.
2. Related Work
…
어떠한 3D supervision 또는 camera extrinsics를 요구하지않는 것은 오로지 EpipolarPose와 Drover et al.’s method뿐이다. 다른것들은 image features를 사용하지 않지만, EpipolarPose는 image features와 epipolar geometry 모두 사용하고 더욱 정확한 결과를 생산한다.
3. Models and methods
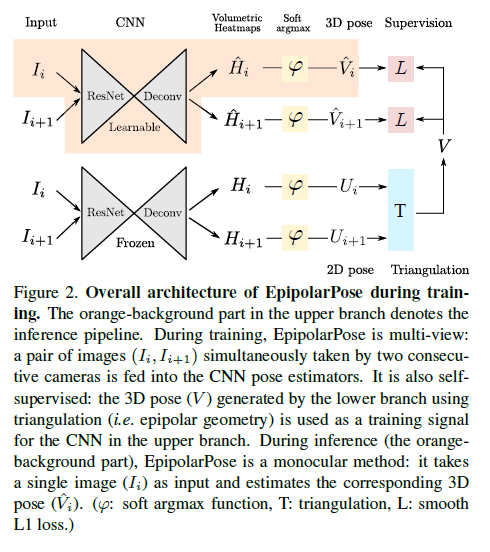
우리가 제안한 method의 전반적인 training pipeline,EpipolarPose는 Figure2에서 보여준다.
orange-background part는 inference pipeline을 보여준다.
EpipolarPose의 training에서, setup은 다음과 같이 가정한다.
scene에서 동시에 사람 사진을 찍는 n camera(_n_은 무조건 2이상)가 있다.
이 cameras는 1부터 _n_까지 id numbers를 부여한다, 연속한 cameras들은 각각에 가깝다.
cameras들은 각각 images \(I_1,I_2,...,I_n\)를 생산한다.
그런다음, 연속적인 image pairs, \(\{(I_i,I_{i+1}) \vert i=1,2,...,n-1\}\)는 training examples를 형성한다.
3.1. Training
EpipolarPose의 training pipeline (Figure 2) 에서, 같은 pose estimation network에서 각각 시작하는 2개의 branches가 있다.
이 networks는 MPII Human Pose dataset (MPII)에 pre-trained 된 networks이다. training하는동안, pose estimation network의 위 branch만 trained 된다; 다른 하나는 frozen 시킨다.
EpipolarPose는 camera 2개이상을 사용하여 train 될 수 있지만 단순화 하기 위해, 여기서 우리는 n = 2인 training pipeline을 설명하겠다.
n=2에서, 각 training example은 오로지 하나의 image pair만 포함한다.
Images \(I_i\)와 \(I_{i+1}\)은 3D (upper) branch와 2D (lower) branch pose estimation networks 둘 다에 먹인다, volumetric heatmaps \(\hat{H}\)을 얻기위해, \(H \in \mathbb{R}^{w \times h \times d}\), 각각이 \(w,h\)는 deconvolution이후 spatial size이고, \(d\)는 hyperparameter로 정의된 depth resolution이다.
soft argmax activation function \(\varphi(.)\)를 적용한 후에, 우리는 3D pose \(\hat{V} \in \mathbb{R}^{J \times 3}\) 그리고 2D pose \(U \in \mathbb{R}^{J \times 2}\) outputs를 얻는다(,J는 body joints의 수).
주어진 volumetric heatmap에서, 하나는 (모든 3 dimensions에서 softargmax를 적용함으로써)3D pose와 (오로지 x,y에 softargmax를 적용함으로써)2D pose를 얻을 수 있다. 2D pose branch의 output으로써, 우리는 global coordinate frame에서 3D human pose \(V\)를 얻기를 원한다.
\(i^{th}\)번째 image에서 \(j^{th}\) joint의 2D coordinate가 \(U_{i,j}=[x_{i,j},y_{i,j}]\)라고 하고 3D coordinate는 \([X_j,Y_j,Z_j]\)라고 하자, 우리는 pinhole image projection model을 가정하여 그것들 사이의 관계를 설명할 수 있다.
\(\begin{bmatrix} x_{i,j} \\ y_{i,j} \\ w_{i,j} \end{bmatrix} = K[R \vert RT] \begin{bmatrix} X_{j} \\ Y_{j} \\ Z_{j} \\1 \end{bmatrix}\) , \(K = \begin{bmatrix} f_x & 0 & c_x \\ 0 & f_{y} & c_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\), \(T = \begin{bmatrix} T_{x} \\ T_{y} \\ T_{z} \end{bmatrix}\)
여기서 \(w_{i,j}\)는 camera reference frame과 관련된 \(i^{th}\)번째 camera의 image에서 \(j^{th}\)번째 joint의 depth이고, K는 camera intrinsic parameters(즉, focal length \(f_x\)와 \(f_y\), principal point \(c_x\) and \(x_y\))로 encode되고, R과 T는 rotation과 translation의 camera extrinsic parameters이다.
우리는 simplicity(단순성)을 위해 camera distortion(카메라 왜곡)을 생략한다.
보통 dynamic capture environments인 경우인, camera extrinsic parameters가 사용가능하지 않을때, 우리는 body joints를 calibration targets로 사용할 수 있다.
우리는 첫번째 camera를 coordinate system의 중심으로 가정한다, 이것은 첫번째 camera의 R이 identity matrix를 의미한다.
image plane에서 \(U_i\)와 \(U_{i+1}\)의 해당 joints의 경우, 우리는 RANSAC algorithm을 이용하여 \(\forall_j\)에 대해 \(U_{i,j}FU_{i+1,j}=0\)을 만족하는 fundamental matrix F를 찾는다.
F에서부터, 우리는 \(E=K^TFK\)에 의해 essential matrix E를 계산한다.
SVD로부터 E를 decomposing함으로써, R에 대한 4가지 가능한 solutions를 얻는다.
cheirality check를 함으로써 possible pose hypotheses를 검증하여 옳은 하나를 결정한다.
cheirality check는 triangulated 3D points가 positive depth(양의 깊이)를 갖여야한다는 것을 의미한다[26].
우리의 모델이 normalized poses를 ground truth로 사용하기 때문에, training중 scale은 생략한다.
마지막으로 synchronised 2D images에 상응하는 3D pose V를 얻기 위해 다음과 같이 triangulation을 사용한다 (즉, epipolar geometry).
어디에도 occluded가 없는 \((I_i,I_{i+1})\)에 모든 joints에 대해, polynomial triangulation [12]를 이용하여 3D point \([X_j, Y_j, Z_j]\)를 triangulate한다.
2개 이상의 cameras settings에서, 우리는 median 3D postion을 찾기위해 vector-median을 계산한다.
upper (3D) branch에서 예측한 camera frame에서의 3D pose간의 loss를 계산하기위해, V를 상응하는 camera space에 project한다, 그런다음 3D branch를 학습하기 위해 \(\text{smooth}_{L_1}(V-\hat{V})\)를 최소화 한다 : \[f(n)= \begin{cases} 0.5x^2, & \text{if } |x| < 1 \\ |x| - 0.5, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}\]
Why do we need a frozen 2D pose estimator?
EpipolarPose의 training pipeline에는 pose estimator로 각각 시작하는 2개의 branches가 있다.
upper branch에서 estimator는 trainable하지만 다른 하나인 lower branch는 frozen한다.
lower branch estimator의 역할은 2D poses를 생산하는 것이다.
trainable upper branch에서도 2D pose를 얻을수 있기 때문에 frozen estimator의 필요성에 의문을 제기할수 있다.
우리가 그렇게 하려고 했을 때, 우리의 방법은 모든 keypoints들이 single location으로 collapse하는 degenerate solutions을 만들어냈다.
다른 multi-view methods들도 같은 문제에 직면했었다[31,37].
Rhodin et al. [31]는 small set of gt examples를 사용함으로써 이 문제를 해결하였지만, 이러한 gt를 얻는것은 대부분의 in the wild settings에서 실현 가능하지 않다.
최근에 제안된 또 하나의 solution [37]은 estimated relative rotaion \(\hat{R}\) (두개의 keypoints sets의 Procrusters alignment를 통한 계산됨)과 groud truth R 간의 angular distance를 최소화 하는것이다.
그럼에도 불구하고 dynamic capture setups에서 groud truth R을 얻는것은 어렵다.
이런 단점을 극복하기 위해, 오로지 training동안 frozen 2D pose detector를 사용한다.
3.2 Inference
Inference는 Figure 2에 orange-background part를 포함한다.
input은 single image이고 output은 soft-argmax activation, \(\varphi(.)\)에 의해 얻은 estimated 3D pose \(\hat{V}\)이다. on 3D volumetric heatmap \(\hat{H}_i\)
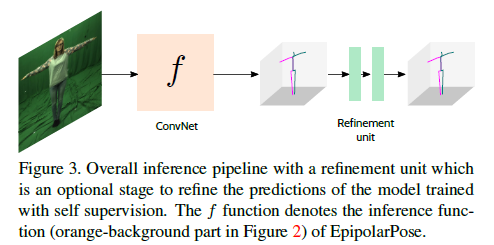
3.3 Refinement, an optional post-training
detected 2D keypoints를 3D joints로 lift하는 몇몇 기술 [22,11,39]가 있다.
이 methods는 random camera projections를 시행함으로써 motion capture (MoCap) data로 부터 얻을 수 있는 generalized 2D -> 3D mapping을 학습할 수 있다.
refinement unit (RU)를 우리의 self supervised model을 통합하는것은 pose estimation accuracy를 더욱 개선할 수 있다.
이 방법에서, 어떤 라벨 없이 multiple view footages를 구성하는 his/her own data에 EpipolarPose를 train할수 있고 더욱 향상된 결과를 위해 이것을 RU와 통합한다.
그것을 가능하게 하기위해, EpipolarPose로부터 noisy 3D detections를 받아들이기 위해 RU의 input layer를 수정하고 그것이 refinement strategy를 학습할 수 있게 한다.(Figure 3)
전반적인 RU architecture는 [22, 11]에 의해 영감을 받았다.
그것은 3D noisy inputs를 더 reliable 3D pose predictions로 map하기위해 2개의 computation blocks을 가지는데 이것은 certain linear layers이고 이 다음 Batch Normalization [14], Leaky ReLU [21] activation 그리고 Dropout layers로 이어진다.
layers간 information flow를 용이하게 하기위해, residual connections를 추가하였고 supervision에 intermediate layers의 접근을 용이하게 하기위해 intermediate loss를 적용하였다.
